Ingest Google Cloud metrics
This feature isn't available to all Chronosphere Observability Platform users and might not be visible in your app. For information about enabling this feature in your environment, contact Chronosphere Support.
Google Cloud (opens in a new tab) integration connects Chronosphere Observability Platform with Google Cloud to ingest metrics from Google Cloud projects.
Observability Platform uses Google's service account impersonation (opens in a new tab) as the authentication mechanism to connect Google Cloud with Observability Platform. Service account impersonation is trust-based, and uses short-lived credentials so that one Google Cloud service account principal can impersonate another.
Use the Google Cloud Integration Dashboard to review the status of your integration.
Set up Google Cloud integration
-
Request infrastructure from Chronosphere.
Chronosphere Support must create infrastructure for your Google Cloud integration for use with your tenant. Before proceeding, contact Chronosphere Support.
-
Modify the Google Cloud domain restriction constraint.
If your Google Cloud organization restricts identities by domain (opens in a new tab), you must add the Observability Platform customer identity (
C04aozwp9) as an allowed value in your policy. -
Create a Google Cloud service account.
A Google Cloud service account isn't an Observability Platform service account. Observability Platform requires a Google Cloud service account in the user's Google Cloud project to provide Observability Platform access to metrics using service account impersonation.
For each Google Cloud project, create a service account (opens in a new tab) with the
monitoring.viewerrole.To instead grant a more restricted set of permissions, implementing the principle of least privilege, create a custom role with permissions for
monitoring.timeSeries.listandmonitoring.metricDescriptors.list. -
Add the Observability Platform principal to the Google Cloud service account.
Each Google Cloud service account must grant access to the Observability Platform principal to impersonate them. The Observability Platform principal format is:
gcp-metrics-<tenant-name>@chronosphere-production-a|b|c.iam.gserviceaccount.comYour cluster can vary (
a,b, orc). Check with your account team to ensure you have the correct format.Grant the principal the
iam.serviceAccountTokenCreatorrole. -
Configure the integration in Observability Platform.
Initialize the integration using the Google Cloud integration API by applying the configuration with Chronoctl or Terraform.
For each Google Cloud project, supply the Google Cloud service account email (SERVICE-ACCOUNT@PROJECT-ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com) in the request to configure the integration, along with specific metrics to ingest using metric prefixes. See Metric Prefix Search for examples.
Example configuration
The following code provides an example for creating a single Google Cloud service account in the user's Google Cloud project, and enables Observability Platform to impersonate and gain access.
locals {
// Email address of Observability Platform tenant-specific principal.
chronosphere_sa_email = "SERVICE-ACCOUNT@PROJECT-ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
// Google Cloud project containing monitoring data to be ingested into
// Observability Platform.
monitoring_project_id = "PROJECT_ID"
}
// Service account that will allow Observability Platform tenant-specific principal
// to impersonate it.
resource "google_service_account" "chronosphere" {
project = local.monitoring_project_id
account_id = "chronosphere"
}
// Custom role with minimal set of permissions for principle of least privilege
// resource "google_project_iam_custom_role" "chronosphere" {
project = local.monitoring_project_id
role_id = "Google Cloud Integration Metrics Viewer"
title = "Google Cloud Integration Metrics Viewer"
description = "Role for granting view access for Google Cloud integration"
permissions = [
"monitoring.metricDescriptors.list",
"monitoring.timeSeries.list",
]
}
// The service account has the minimal set of permissions for access to the project
// containing the metric data so that it can retrieve time series data from the
// Google Cloud API.
resource "google_project_iam_member" "chronosphere" {
project = local.monitoring_project_id
role = google_project_iam_custom_role.chronosphere.id
member = google_service_account.chronosphere.member
}
// The service account provides the Observability Platform tenant-specific principal with
// roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator access so that it can impersonate it. Only
// the Observability Platform tenant-specific principal will be able to perform this
// impersonation.
data "google_iam_policy" "chronosphere" {
binding {
role = "roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator"
members = ["serviceAccount:${local.chronosphere_sa_email}"]
}
}
// Assign the token creator permission to the service account.
resource "google_service_account_iam_policy" "chronosphere" {
service_account_id = google_service_account.chronosphere.name
policy_data = data.google_iam_policy.chronosphere.policy_data
}
Use metrics scopes for projects
Chronosphere encourages users to use metrics scoping for projects (opens in a new tab) in their Google Cloud environment, particularly for users that manage five or more Google Cloud projects.
Chronosphere recommends creating a new metrics scoped project for use with metrics ingestion. Using a new scoped project minimizes the impact on your existing workload.
Metrics scopes have benefits over configuring individual Google Cloud projects for Google Cloud integration:
-
Google Cloud API cost savings: With metrics scoping, Observability Platform ingests metrics using the least number of API requests to Google Cloud. Metrics scoped projects introduce a fan in/out model of ingesting metrics from the underlying Google Cloud projects that will pack time series data points for each metric into the smallest set of API responses. The Google Cloud API cost savings are significant, particularly for users managing multiple Google Cloud projects.
-
Configuration simplicity: With metrics scoping, users can manage a smaller set of Google Cloud service accounts and configuration in Observability Platform. This simplifies management of the Google Cloud integration.
Set up Observability Platform to receive Google Cloud data
After configuring Google Cloud to enable Observability Platform to access metrics, you must configure Observability Platform to receive and process those metrics.
View Google Cloud integrations
To list or view Google Cloud integrations, use one of the following options:
To list your Google Cloud integrations:
chronoctl gcp-metrics-integrations listTo view a Google Cloud integration with Chronoctl, use the command:
chronoctl gcp-metrics-integrations read SLUGReplace SLUG with the unique identifier of the Google Cloud integration.
Create or update a Google Cloud integration
You can create or update your Google Cloud integration with Observability Platform by applying a configuration file with Chronoctl or Terraform. Your must add your service account to an Observability Platform team with SysAdmin permissions.
To create a Google Cloud integration with Chronoctl, use the command:
chronoctl gcp-metrics-integrations create --filename FILENAMEReplace FILENAME with the name of your Chronoctl configuration file.
To update a Google Cloud integration with Chronoctl, use the command:
chronoctl gcp-metrics-integrations update --filename FILENAMEReplace FILENAME with the name of your Chronoctl configuration file.
The input file uses the following structure:
api_version: v1/config
kind: GcpMetricsIntegration
spec:
name: NAME
slug: SLUG
service_account:
client_email: EMAIL
metric_groups:
- project_id: PROJECT_ID
prefixes:
- PREFIXReplace the following:
NAME: (string) The name of the Google Cloud integration.SLUG: (string) The unique identifier of the Google Cloud integration.EMAIL: (string) The email address of the customer's Google Cloud service account of the formSERVICE_ACCOUNT@PROJECT-ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com.PROJECT_ID: (string) The ID of the customer's Google Cloud project to ingest metrics from.PREFIX: (list(string)) A list of metric prefixes to ingest from the Google Cloud project.
Delete a Google Cloud integration
Delete a Google Cloud integration using one of the following methods:
To delete a Google Cloud integration with Chronoctl, your account must have SysAdmin permissions. Use the command:
chronoctl gcp-metrics-integrations delete SLUGMetric information
The following sections contain information about Google Cloud metrics information and how Observability Platform uses or displays it.
Metrics availability
Google metrics have different stages of availability (opens in a new tab). Observability Platform prioritizes metrics Google considers Generally Available (GA). Non-GA metrics ingest on a best-effort basis, and might not provide stable data.
On average, Google Cloud metrics display in Observability Platform with a delay on the order of minutes from the metric timestamp in Google Cloud. These metrics appear delayed due to the following factors:
-
Latency delay: Most Google Cloud metrics have a delay (opens in a new tab) before they're made available for querying by Google Cloud API.
Metrics with an ingest delay exceeding seven hours won't be ingested into Chronosphere. For example, Firebase database metrics can exceed this latency delay and won't be ingested.
-
Sample rate: Google Cloud metrics sample (opens in a new tab) at different rates. Most metrics sample at 60-second intervals, with some as long as once per day.
Due to these delays, configure monitors to expect a delay in arrival. Use the PromQL offset modifier (opens in a new tab) to account for delays.
Observability Platform doesn't ingest the following networking flow metric prefixes due to their unpredictable data volumes and cardinality. If you have a specific need for metrics using these prefixes, contact Chronosphere Support.
networking.googleapis.com/pod_flownetworking.googleapis.com/vm_flownetworking.googleapis.com/node_flow
Metric names
In Observability Platform, Google Cloud metrics (opens in a new tab) have the following name structure:
gcp_<MONITORED-RESOURCE-NAME>_<FULLY-QUALIFIED-METRIC-NAME>where:
-
MONITORED-RESOURCE-NAMEis the monitored resource type (opens in a new tab) in Google Cloud. -
FULLY-QUALIFIED-METRIC-NAMEis the metric name in Google Cloud, with characters like.and/convert to_to be Prometheus compatible. The following examples are fully qualified metric names in Google Cloud before metric name sanitization:bigquery.googleapis.com/job/num_in_flightcloudsql.googleapis.com/database/available_for_failoverkubernetes.io/container/accelerator/memory_total
The following is an example of how to map a CloudSQL metric name in Google Cloud to a metric name in Observability Platform:
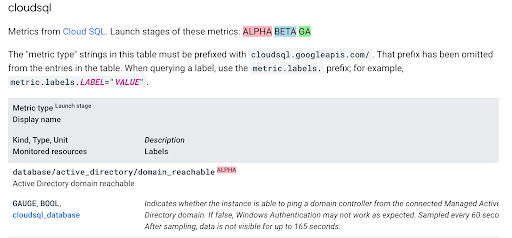
For this metric, cloudsql_database is the monitored resource name and
cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/active_directory/domain_reachable is the fully
qualified metric name. In Observability Platform, the metric name is
gcp_cloudsql_database_cloudsql_googleapis_com_database_active_directory_domain_reachable.
Finding Google Cloud metrics in Metrics Explorer
Use Metrics Explorer to find and review the status of your ingested metrics.
-
All Google Cloud metrics start with the prefix
gcp_. Searching for this prefix displays all Google Cloud metrics in the platform. -
Substring search is possible. For example, if the original Google Cloud metric name contains a substring like
domain_reachable, searching for the substring returns the Google Cloud metric, along with other metrics containing the substring.
Metric mappings
Google Cloud metrics map closely to Observability Platform metric types. Metric mappings are defined on the metric types page.
Metric prefix search
Google Cloud integration scrapes metrics by metric prefix search using the Monitoring Query Language (MQL) (opens in a new tab). This following table provides configuration examples for Google Cloud integration:
| Metric Prefix | Description | Example Metrics |
|---|---|---|
cloudsql.googleapis.com/ | Ingest all CloudSQL metrics | cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/active_directory/domain_reachable cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/active_directory/instance_available cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/data_cache/bytes_used cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/uptime |
cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/ | Ingest all CloudSQL metrics starting with database/ | cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/active_directory/domain_reachable cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/active_directory/instance_available cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/data_cache/bytes_used cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/uptime |
bigquery.googleapis.com/s | Ingest all BigQuery metrics starting with s | bigquery.googleapis.com/slots/allocated bigquery.googleapis.com/slots/allocated_for_reservation bigquery.googleapis.com/storage/insertall_inserted_rows bigquery.googleapis.com/storage/uploaded_row_count |
cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/up | Ingest all CloudSQL metrics starting with database/up | cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/up cloudsql.googleapis.com/database/uptime |
b | Ingest all metrics starting with b | backupdr.googleapis.com/protected_data/volume bigquery.googleapis.com/slots/allocated bigtable.googleapis.com/backup/bytes_used |